cse-15l-lab-report
Lab Report 2 - Servers and SSH Keys (Week 3)
Part 1 - Servers
A server is basically a computer like the one you are using now, but it specializes in managing network resources.
For this lab we had written our own server in Java. This webserver is called ChatServer. It’s goal is to take in two parameters s=<String> and user=<String> then concatenate them to be a single string with the fromat user: s.
For more info on the instructions visit here.
Here is the code I wrote:
ChatServer.java
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.URI;
import java.util.ArrayList;
class Handler implements URLHandler {
ArrayList<String> messages = new ArrayList<>();
public String handleRequest(URI url) {
if (url.getPath().equals("/")) {
return messagesToString();
} else if (url.getPath().equals("/add-message")) {
String[] parameters = url.getQuery().split("&");
String s_param = parameters[0].split("=")[1];
String user_param = parameters[1].split("=")[1];
//check if parameters match otherwise it will be null
String message = null;
String user = null;
if ("s".equals(s_param[0])){
message = s_param[1];
}
if ("user".equals(user_param[0])){
user = user_param[1];
}
messages.add(user + ": " + message);
// edit below
} else {
return "404 Not Found!";
}
}
public String messagesToString(){
String total = "";
for (String message : messages){
total += message + "\n";
}
return total;
}
}
class ChatServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
if(args.length == 0){
System.out.println("Missing port number! Try any number between 1024 to 49151");
return;
}
int port = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
Server.start(port, new Handler());
}
}
Now that we have written, compiled and launched our server we can now start testing.
For reference we had launched the server on: http://localhost:5000/
Screenshot 1
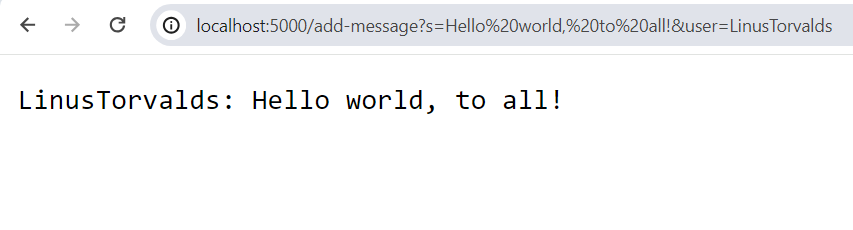
Input:
http://localhost:5000/add-message?s=Hello%20world,%20to%20all!&user=LinusTorvalds
Output:
Which methods were called in the code?
String handleRequest(URI url)String messagesToString()String getPath()boolean equals(Object compared)String[] split(String regex)
What are the relevant arguments to those methods, and the values of any relevant fields of the class?
String handleRequest(URI url)- This method allows us to interact with the URL and it’s arguments. It then looks for the
/add-messagecommand. It then looks at two queries and their contents, in this case?s=Hello%20world,%20to%20all!and&user=LinusTorvalds. This is then concatenated into"LinusTorvalds: Hello world, to all!and then this is added toArrayList<String> messages. - A relevant argument that is passed is
URI url. URI stands for Uniform Resource Identifier, which is our host url. So in our case itslocalhost:5000. Theurlobject can get the queries that the user typed.
- This method allows us to interact with the URL and it’s arguments. It then looks for the
String getPath(): We had used this to get the arguments that user put in this case its/add-message?s=Hello%20world,%20to%20all!&user=LinusTorvalds.boolean equals(Object compare): We us this to find the command/add-messageand all the arguments that the user inputted.String[] split(String regex): We had used this to extract the arguments from the String we get fromgetPath()in order to process it to be added to themessagesarray.-
ArrayList<String> messages: This is a field. A concatenated String is added into this ArrayList and expands. String messagesToString()- This method acesses
ArrayList<String> messagesthen goes through all of the items and then concatenates all of them into a singular string. This is so the web page can return all of the messaging content, but nothing changes. - A field variable accessed is
ArrayList<String> messages
- This method acesses
How do the values of any relevant fields of the class change from this specific request? If no values got changed, explain why.
- A value that gets changed is
ArrayList<String> messages. This is because it had added a processed version of the users parameters from the URL intomessages. It addsLinusTorvalds: Hello world, to all!. String parameters[]becomes{"s=Hello world, to all!", "user=LinusTorvalds"}(note the %20’s are the encoding for the space character in a URL)String s_param: this becomes"Hello world, to all!"String user_param: this becomes"LinusTorvalds"
Screenshot 2
Input:
http://localhost:5000/add-message?s=Hey%20Linus,%20whats%20up.&user=Kayne
Output:
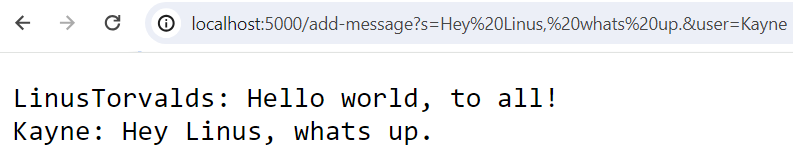
Which methods were called in the code?
String handleRequest(URI url)String messagesToString()String getPath()boolean equals(Object compared)String[] split(String regex)
What are the relevant arguments to those methods, and the values of any relevant fields of the class?
- This one uses all the same methods.
String handleRequest(URI url)- This method allows us to interact with the URL and it’s arguments. It then looks for the
/add-messagecommand. It then looks at two queries and their contents, in this case?s=Hello%20world,%20to%20all!and&user=LinusTorvalds. This is then concatenated into"LinusTorvalds: Hello world, to all!and then this is added toArrayList<String> messages. - A relevant argument that is passed is
URI url. URI stands for Uniform Resource Identifier, which is our host url. So in our case itslocalhost:5000. Theurlobject can get the queries that the user typed.
- This method allows us to interact with the URL and it’s arguments. It then looks for the
String getPath(): We had used this to get the arguments that user put in this case its/add-message?s=Hello%20world,%20to%20all!&user=LinusTorvalds.boolean equals(Object compare): We us this to find the command/add-messageand all the arguments that the user inputted.String[] split(String regex): We had used this to extract the arguments from the String we get fromgetPath()in order to process it to be added to themessagesarray.ArrayList<String> messages: This is a field. A concatenated String is added into this ArrayList and expands.
How do the values of any relevant fields of the class change from this specific request? If no values got changed, explain why.
- A value that gets changed is
ArrayList<String> messages. This is because it had addedKayne: Hey Linus, whats up.to the ArrayList. String parameters[]becomes{"s=Hey Linus, whats up.", "user=Kayne"}(note the %20’s are the encoding for the space character in a URL)String s_param: this becomes"Hey Linus, whats up."String user_param: this becomes"Kayne"
Part 2 - SSH
SSH’ing into a system can be quite annoying, having to type in your password everytime you have to access it. We can circumvent this by using the ssh-keygen command. We genearte a key without a passphrase then use the scp (Secure Copy) to copy the public key to the remote device.
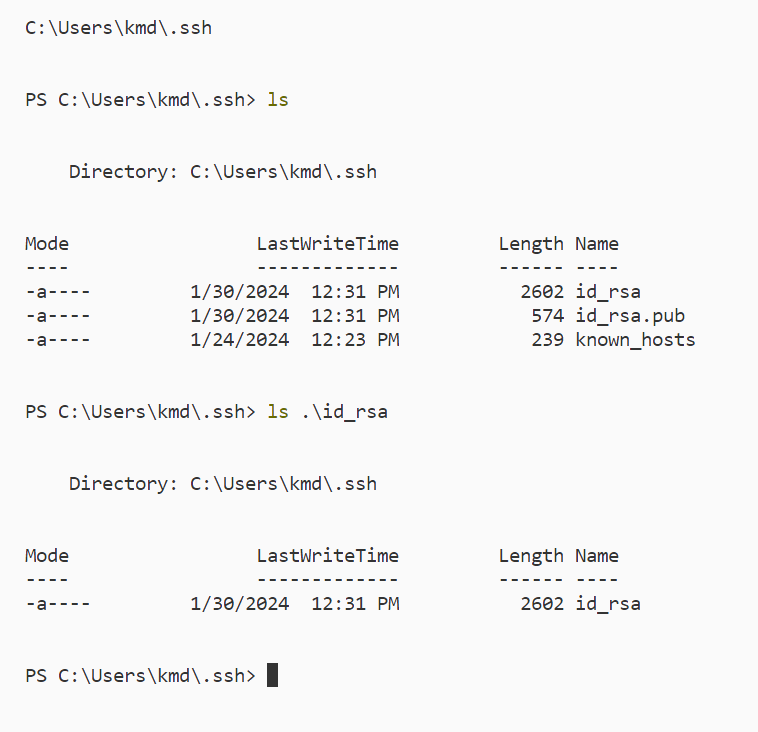
This is where our private key is located. (it is located on our device that we are currently using)
This is where our public key is located. (it is located on the remote device that we are connected to)
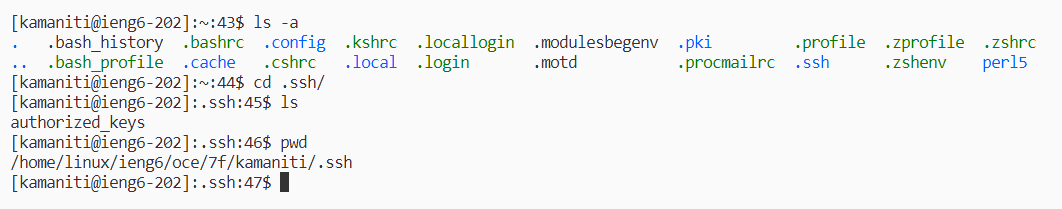
Now we are able to connect using sshto the device kamaniti@ieng6.ucsd.edu without the need for a password.
Here is an example of me doing this. As you can see it didn’t ask for any password, it had just just logged me into the system.
#
Part 3 - Summary
In a couple of sentences, describe something you learned from lab in week 2 or 3 that you didn’t know before.
During the lab’s week 2 and 3 I had learend about a really useful command called man. This is short for manual. What it does is it exeutes man <command> which will prompt up documentation on how to use the command.
For example if we use it on:
man ls
Then we get the output:
NAME
Get-ChildItem
SYNTAX
Get-ChildItem [[-Path] <string[]>] [[-Filter] <string>] [-Include <string[]>] [-Exclude <string[]>] [-Recurse] [-Depth <uint32>] [-Force] [-Name] [-UseTransaction] [-Attributes
{ReadOnly | Hidden | System | Directory | Archive | Device | Normal | Temporary | SparseFile | ReparsePoint | Compressed | Offline | NotContentIndexed | Encrypted |
IntegrityStream | NoScrubData}] [-FollowSymlink] [-Directory] [-File] [-Hidden] [-ReadOnly] [-System] [<CommonParameters>]
Get-ChildItem [[-Filter] <string>] -LiteralPath <string[]> [-Include <string[]>] [-Exclude <string[]>] [-Recurse] [-Depth <uint32>] [-Force] [-Name] [-UseTransaction]
[-Attributes {ReadOnly | Hidden | System | Directory | Archive | Device | Normal | Temporary | SparseFile | ReparsePoint | Compressed | Offline | NotContentIndexed | Encrypted |
IntegrityStream | NoScrubData}] [-FollowSymlink] [-Directory] [-File] [-Hidden] [-ReadOnly] [-System] [<CommonParameters>]
ALIASES
gci
-- To download and install Help files for the module that includes this cmdlet, use Update-Help.
-- To view the Help topic for this cmdlet online, type: "Get-Help Get-ChildItem -Online" or
go to https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkID=113308.
This is the documentation of the ls command and how to use it. This command will be very useful for this class in the case that we run into a command that we don’t know. With this command all I need to do is run man.